Back to all publications...
Deep hashing using entropy regularised product quantisation network
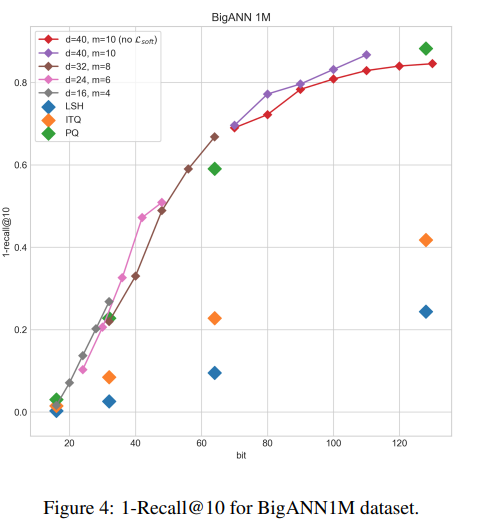
In large scale systems, approximate nearest neighbour search is a crucial algorithm to enable efficient data retrievals. Recently, deep learning-based hashing algorithms have been proposed as a promising paradigm to enable data dependent schemes. Often their efficacy is only demonstrated on data sets with fixed, limited numbers of classes. In practical scenarios, those labels are not always available or one requires a method that can handle a higher input variability, as well as a higher granularity. To fulfil those requirements, we look at more flexible similarity measures. In this work, we present a novel, flexible, end-to-end trainable network for large-scale data hashing. Our method works by transforming the data distribution to behave as a uniform distribution on a product of spheres. The transformed data is subsequently hashed to a binary form in a way that maximises entropy of the output, (i.e. to fully utilise the available bit-rate capacity) while maintaining the correctness (i.e. close items hash to the same key in the map). We show that the method outperforms baseline approaches such as locality-sensitive hashing and product quantisation in the limited capacity regime.
Jo Schlemper, Jose Caballero, Andy Aitken, Joost van Amersfoort
arXiv
[paper]