Back to all publications...
Prioritized Training on Points that are Learnable, Worth Learning, and not yet Learnt
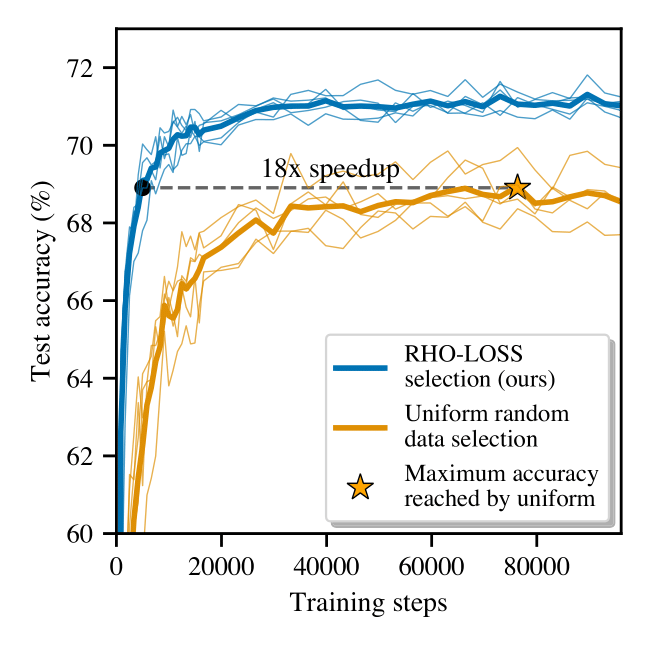
Training on web-scale data can take months. But much computation and time is wasted on redundant and noisy points that are already learnt or not learnable. To accelerate training, we introduce Reducible Holdout Loss Selection (RHO-LOSS), a simple but principled technique which selects approximately those points for training that most reduce the model’s generalization loss. As a result, RHO-LOSS mitigates the weaknesses of existing data selection methods: techniques from the optimization literature typically select “hard” (e.g. high loss) points, but such points are often noisy (not learnable) or less task-relevant. Conversely, curriculum learning prioritizes “easy” points, but such points need not be trained on once learned. In contrast, RHO-LOSS selects points that are learnable, worth learning, and not yet learnt. RHO-LOSS trains in far fewer steps than prior art, improves accuracy, and speeds up training on a wide range of datasets, hyperparameters, and architectures (MLPs, CNNs, and BERT). On the large web-scraped image dataset Clothing-1M, RHO-LOSS trains in 18x fewer steps and reaches 2% higher final accuracy than uniform data shuffling.
Sören Mindermann, Jan Brauner, Muhammed Razzak, Mrinank Sharma, Andreas Kirsch, Winnie Xu, Benedikt Höltgen, Aidan Gomez, Adrien Morisot, Sebastian Farquhar, Yarin Gal
ICML, 2022 [Paper]